




Var01.java
public class Var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//声明变量
int a;
a = 100;
System.out.println(a);
//还可以这样使用
int b = 800;
System.out.println(b);
}
}

Var02.java
public class Var02 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//记录人的信息
int age = 30;
double score = 88.8;
char gender = '男';
String name = "king";
//输出信息
System.out.println("人的信息如下:");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(score);
System.out.println(gender);
}
}

VarDetail.java
public class VarDetail {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//变量必须先声明,后使用,即有顺序
int a = 50;
System.out.println(a);//50
//该区域的数据/值可以在同一类型范围内不断变化
//a = "jack" // 错误
a = 88;
System.out.println(a);//88
//变量在同一个作用域内不能重名
// int a = 77;//错误
}
}
class Dog {
public static void main(String[] args){
int a =99;
System.out.println(a);
}
}

Plus.java
public class Plus {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(100 + 98);
System.out.println("100" + 98);
System.out.println(100 + 3 + "hello");
System.out.println("hello" + 100 + 3);
}
}


IntDetail.java
public class IntDetail {
public static void main(String[] args){
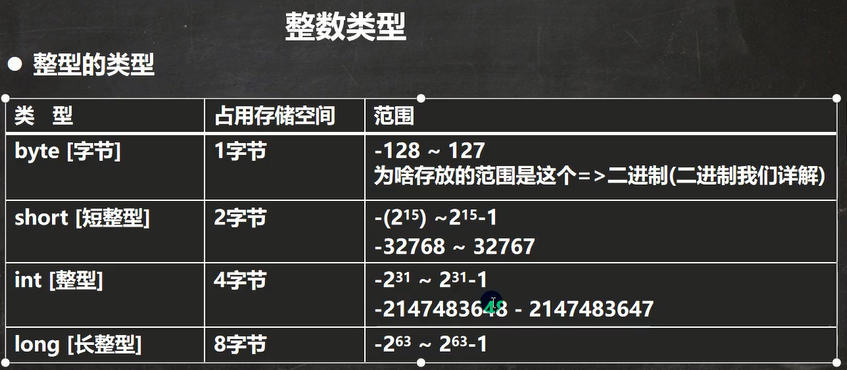
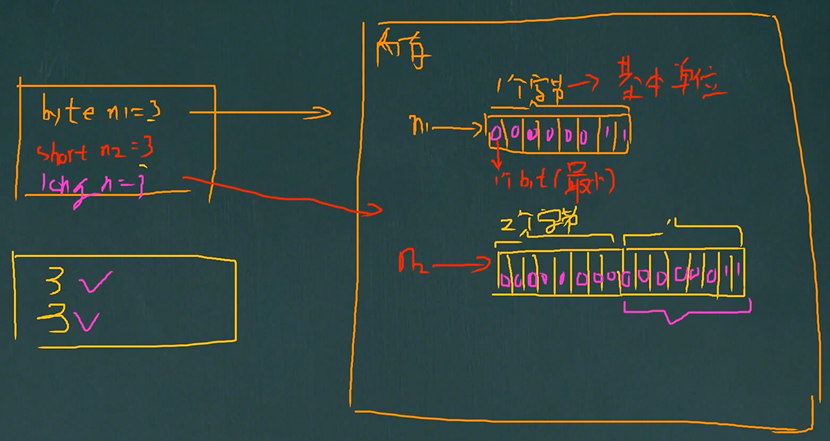
//Java的整型常量(具体值)默认为int型,声明long型常量须后加"l"或"L"
int n1 = 1;
Long n2 = 88L;
}
}


FloatDetail.java
public class FloatDetail {
public static void main(String[] args){
//Java的浮点型常量(具体值)默认为double型,声明float型常量,须后加‘f’或‘F’
// float num1 = 1.1;//错误
float num2 = 1.2F;
double num3 = 1.3;
double num4 = 1.3F;
System.out.println(num2);//1.2
System.out.println(num3);//1.3
System.out.println(num4);//1.299...
//十进制数形式:如:5.12 512.0f .512 (必须有小数点)
double num5 = .123; //等价0.123
System.out.println(num5);//0.123
//科学计数法形式:如:5.12e2 [5.12*10的2次方] 5.12E-2 [5.12/10的2次方]
System.out.println(5.12e2);//512.0
System.out.println(5.12E-2);//0.0512
//通畅情况下,应该是用double型,因为它比float型更精准。
//举例说明
double num9 = 2.1234567851;
float num10 = 2.1234567851F;
System.out.println(num9);//2.1234567851
System.out.println(num10);//2.12345678
//浮点数使用陷阱:2.7 和8.1/3 比较
double num11 = 2.7;
double num12 = 8.1 / 3;
System.out.println(num11);//2.7
System.out.println(num12);//2.699...接近2.7的一个小数,而不是2.7
// 得到一个重要的一个使用点:当我们对运算结果是小数的进行相等判断时,会有错误
//应该是以两个数的差值的绝对值,在某个精度范围内判断
if(num11 == num12){
System.out.println("相等");
}
// 可以通过Java API 来查看
System.out.println(Math.abs(num11 - num12));//4.440892098500626E-16
//正确的写法
if(Math.abs(num11 - num12) < 0.000001){
System.out.println("差值到达规定精度,相等");
}
}
}


Char01.java
//演示char的基本使用
//
public class Char01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = '\t';
char c3 = '郭';
char c4 = 97;字符类型可以直接存放一个数字
System.out.println(c1);//a
System.out.println(c2);//
System.out.println(c3);//郭
System.out.println(c4);//a 当输出c4的时候,会输出97表示的字符=>编码的概念,会输出a
}
}

CharDetail.java
public class CharDetail {
// 编写一个main
public static void main(String[] args){
//在java中,char的本质是一个整数,在输出时,是unicode码对应的字符
char c1 = 97;
System.out.println(c1); //输出a
//要输出对应的数字,可以(int)字符
char c2 = 'a';//输出‘a’对应的数字
System.out.println((int)c2);
char c3 = '郭';
System.out.println((int)c3);//37101
char c4 = 37101;
System.out.println(c4);//郭
//char类型是可以进行运算的,相当于一个整数,因为它都有对应的unicode码。
System.out.println('a' + 10);//107
//课堂小测试
char c5 = 'b' + 1; //98+1
System.out.println((int)c5); //99
System.out.println(c5); //c(找ASCII表)
}
}






Boolean01.java
public class Boolean01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//演示判断成绩是否通过的案例
//定义一个布尔变量
// boolean isPass = true;
boolean isPass = false;
if (isPass == true) {
System.out.println("考试通过,恭喜");
}else{
System.out.println("考试没有通过,下次努力");
}
}
}

AutoConvert.java
public class AutoConvert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示自动转换
int num = 'a';//ok char -> int
double d1 = 80;//ok int->double
System.out.println(num);//97
System.out.println(d1);//80.0
}
}

AutoConvertDetail.java
//自动类型转换细节
//
public class AutoConvertDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//细节1:有多重类型的数据混合运算时
//系统首先自动将所有数据转换成容量最大的那种数据类型,然后再进行计算
int n1 = 10;
// float d1 = n1 +1.1;//错误,因为n1 + 1.1结果为double类型
double d1 = n1 + 1.1;//正确,因为n1 + 1.1结果为double类型
float d2 = n1 +1.1F;//正确,因为n1 + 1.1结果为float类型
//细节2:当我们把精度(容量)大的数据类型复制给精度(容量)小的数据类型时,就会报错,反之就会进行自动数据类型转换。
// int n2 = 1.1;//错误 double->int
//细节3:(byte,short)和char之间不会相互自动转换
//当把数赋给byte时,先判断该数是否在byte范围内,如果是就可以
byte b1 = 10;//对,byte范围为-128~127
int n2 = 1; //n2是int
// byte b2 = n2;//错误,原因:如果是变量复制,判断类型
// char c1 = b1;//错误,原因:byte不能自动转换成为char
//
//细节4:byte,short,char 他们三者可以计算,在计算时首先转换为int类型
//
byte b2 = 1;
byte b3 = 2;
short s1 = 1;
// short s2 = b2 + s1;//错误,b2+s1结果类型为int
int s2 = b2 + s1;//正确
// byte b4 = b2 + b3;//错误,b2+b3结果类型为int
//细节5:boolean类型不参与转换
//
boolean pass = true;
// int num100 = pass;//错误,boolean不参与类型的自动转换
//细节6:自动提升原则:表达式结果的类型自动提升为操作数中最大类型
//
byte b5 = 1;
short s3 = 100;
int num200 = 1;
float num300 = 1.1F;
float num500 = b5 + s3 + num200 + num300;
System.out.println(num500);
// int num500 = b4 + s3 + num200 + num300;//错误,结果为float类型,不能转为int
}
}

ForceConvert.java
//
public class ForceConvert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示强制类型转换
int n1 = (int)1.9;
System.out.println("n1=" + n1);//n1=1 造成精度损失
int n2 = 2000;
byte b1 = (byte)n2;
System.out.println("b1=" + b1);//b1=-48 造成数据溢出
}
}

ForceConvertDetail.java
public class ForceConvertDetail {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//演示强制类型转换
//
//int x = (int)10*3.5+6*1.5;//编译错误;结果为double类型
int x =(int)(10*3.5+6*1.5);//(int)44.0
System.out.println(x);//结果为44
char c1 = 100;//ok
int m = 100;//ok
// char c2 = m;//错误
char c3 = (char)m;//ok
System.out.println(c3);//100对应的字符d
}
}


StringToBasic.java
public class StringToBasic {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//基本数据类型转换为String
int n1 = 100;
float f1 = 1.1F;
double d1 = 4.5;
boolean b1 = true;
String s1 = n1 + "";
String s2 = f1 + "";
String s3 = d1 + "";
String s4 = b1 + "";
System.out.println(s1 + " " + s2 + " " + s3 + " " + s4);//100 1.1 4.5 true
//100 1.1 4.5 true
//String->对应的基本数据类型
String s5 = "123";
//OOP讲对象和方法的时候会详细说
//解读 使用基本数据类型对应的包装类的相应方法,得到基本数据类型
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(s5);
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(s5);
float num3 = Float.parseFloat(s5);
long num4 = Long.parseLong(s5);
byte num5 = Byte.parseByte(s5);
boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
short num6 = Short.parseShort(s5);
System.out.println("===============");
System.out.println(num1);//123
System.out.println(num2);//123.0
System.out.println(num3);//123.0
System.out.println(num4);//123
System.out.println(num5);//123
System.out.println(num6);//123
System.out.println(b);//true
//把字符串转成字符char ->含义是指 把字符串的第一个字符得到
//解读 s5.charAt(0) 得到s5字符串的第一个字符'1'
System.out.println(s5.charAt(0));
}
}

StringToBasicDetail.java
//演示字符串转基本数据类型的细节
//
public class StringToBasicDetail {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
String str = "123";
//转成int
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(n1);//123
}
}

Homework01.java
public class Homework01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
int n1;
n1 = 13;
int n2;
n2 = 17;
int n3;
n3 = n1 + n2;
System.out.println("n3 = " + n3);//30
int n4 = 38;
int n5 = n4 - n3;
System.out.println("n5 = " + n5);//8
}
}

Homework02.java
public class Homework02 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
char c1 = '\n';//换行
char c2 = '\t';//制表位
char c3 = '\r';//回车
char c4 = '\\';//输出\
char c5 = '1';
char c6 = '2';
char c7 = '3';
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
}
}
Homework03.java
public class Homework03 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
//书名用String保存
String s1 = "西游记";
String s2 = "三国";
System.out.println(s1 + s2);//西游记三国
//性别用char保存
char c1 = '男';
char c2 = '女';
System.out.println(c1 + c2);//字符的本质是整数,结果为码值相加52906
//保存两本书的价格
double d1 = 29.89;
double d2 = 19.118;
System.out.println(d1 + d2);//结果为两个数值相加之和,小数为近似值
}
}
Homework04.java
public class Homework04 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args){
String name = "郭勇";
int age = 18;
double score = 99.98;
char gender = '男';
String hobby = "写代码";
// System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("姓名\t年龄\t成绩\t性别\t爱好\n"
+ name + '\t' + age + '\t' + score + '\t'
+ gender + '\t' + hobby);
}
}
 MySQL学习笔记
MySQL学习笔记