语法
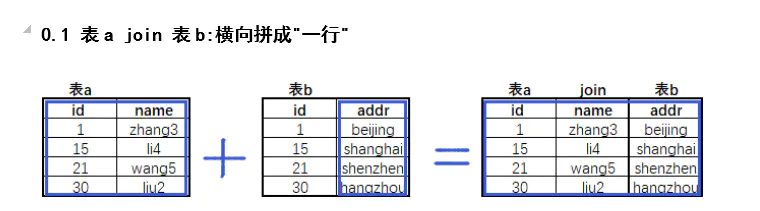
拆开的原因就是减少数据冗余,尽量让数据变成不可再分的结构,即原子结构,多表连接最关键的就是查找表与表之间的连接条件,顺序为先做多表条件,再做where等判断
查询张三的家庭住址
SELECT A.name,B.address FROM from A JOIN B ON A.id=B.id WHERE A.name='zhangsan'
利用world.sql举例
导入数据库world.sql
world.sql下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NL5yx8U22kkv0CXf-KqO6w
提取码:1ze6 [root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p <world.sql
了解表结构,寻找连接条件
desc city; select * from city where population<100; desc country; show create table country; select *from country where code='CHN';
查询一下世界上人口数量小于100人的城市名,国家名,国土面积
select city.name,country.name,country.surfacearea from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where country.population<100;
查询城市shenyang,城市人口,所在国家名(name)及国土面积(SurfaceArea)
select city.name,city.population,country.name,country.surfacearea from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.name='shenyang';
利用列别名查询城市shenyang,城市人口,所在国家名(name)及国土面积(SurfaceArea)
字段别名 select country.name as 国家名, country.SurfaceArea as 国土面积, city.name as 城市名称, city.population as 城市人口 from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.name='shenyang'; 表别名和字段别名 select b.name as 国家名, b.surfacearea as 国土面积, a.name as 城市名称, a.population as 城市人口 from city as a join country as b on a.countrycode=b.code where a.name='shenyang';
利用school.sql举例
1.按照需求创建表结构
use school student :学生表 sno: 学号 sname:学生姓名 sage: 学生年龄 ssex: 学生性别 teacher :教师表 tno: 教师编号 tname:教师名字 course :课程表 cno: 课程编号 cname:课程名字 tno: 教师编号 sc:成绩表 sno: 学号 cno: 课程编号 score:成绩
2.项目构建
drop database school;
create database school charset utf8;
use school;
create table student(
sno int not null primary key auto_increment comment '学号',
sname varchar(20) not null comment '学生姓名',
sage tinyint unsigned not null default 0 comment '学生年龄',
ssex enum('m','f') not null default 'm' comment '性别'
)engine=innodb charset=utf8 comment='学生表';
insert into student(sno,sname,sage,ssex)
values(1,'zhang3',18,'m');
INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES
(2,'zhang4',18,'m'),
(3,'li4',18,'m'),
(4,'wang5',19,'f');
INSERT INTO student
VALUES
(5,'zh4',18,'m'),
(6,'zhao4',18,'m'),
(7,'ma6',19,'f');
INSERT INTO student(sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES
('oldboy',20,'m'),
('oldgirl',20,'f'),
('oldp',25,'m');
desc student;
select * from student;
create table teacher(
tno int not null primary key comment '教师编号',
tname varchar(20) not null comment '教师名字'
)engine=innodb charset=utf8 comment='教师表';
INSERT INTO teacher(tno,tname) VALUES
(101,'oldboy'),
(102,'hesw'),
(103,'oldguo');
desc teacher;
select * from teacher;
create table course(
cno int not null primary key comment '课程编号',
cname varchar(20) not null comment '课程名字',
tno int not null comment '教师编号'
)engine=innodb charset=utf8 comment='课程表';
INSERT INTO course(cno,cname,tno)
VALUES
(1001,'linux',101),
(1002,'python',102),
(1003,'mysql',103);
DESC course;
select * from course;
create table sc(
sno int not null comment '学号',
cno int not null comment '课程编号',
score int unsigned not null default 0 comment '成绩'
)engine=innodb charset=utf8 comment='成绩表';
INSERT INTO sc(sno,cno,score)
VALUES
(1,1001,80),
(1,1002,59),
(2,1002,90),
(2,1003,100),
(3,1001,99),
(3,1003,40),
(4,1001,79),
(4,1002,61),
(4,1003,99),
(5,1003,40),
(6,1001,89),
(6,1003,77),
(7,1001,67),
(7,1003,82),
(8,1001,70),
(9,1003,80),
(10,1003,96);
DESC sc;
select * from sc;
统计zhang3,学习了几门课
select a.sname,count(sc.cno) from student as a join sc on a.sno=sc.sno where a.sname='zhang3';
查询zhang3,学习的课程名称有哪些?
select student.sname,group_concat(course.cname) from student join sc on student.sno=sc.sno join course on sc.cno=course.cno where student.sname='zhang3';
查询oldguo老师教的学生名
select teacher.tname,group_concat(student.sname) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join sc on course.cno=sc.cno join student on sc.sno=student.sno where teacher.tname='oldguo';
查询oldguo所教课程的平均分数
select teacher.tname,avg(sc.score) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join sc on course.cno=sc.cno where teacher.tname='oldguo';
每位老师所教课程的平均分,并按平均分排序
select teacher.tname,avg(sc.score) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join sc on course.cno=sc.cno group by teacher.tname order by avg(sc.score) desc;
扩展:subquery命令
外连接
作用:强制驱动表
驱动表根据on对等关系和contry表next loop(匹配判断)。
驱动表就是在多表连接中,承当for循环中外层循坏的角色,此时,MySQL会拿着驱动表的每个满足条件的关联列的值,去依次找
到for循环中的关联值一一进行判断和匹配。
建议:
1.将结果集小且执行where条件目标结果少的表设置为驱动表更加合适,可以降低next loop的次数。
2.left join可以强制左表为驱动表。
对于内连接来说,我们没办法控制驱动表是谁,完全由优化器绝对顶。如果需要人为干预,需要将内连接写成外连接的方式。
例如:
select city.name,city.population,country.name,country.surfacearea
from city
join country
on city.countrycode=country.code
where city.name='shenyang';
改为:
select city.name,city.population,country.name,country.surfacearea
from city left join country
on city.countrycode=country.code
where city.name='shenyang';
 MySQL学习笔记
MySQL学习笔记