1 课程目标
• 了解 GBase 8c 分布式版本高级语法涵义和使用方法,掌握并熟练使用。
• 存储引擎
• 分区表的各种组合 • 索引多样化
• 数据压缩
• 子事务
2 存储引擎
—2.1 目前支持
• USTORE,表示表支持Inplace-Update 存储引擎。
• ASTORE,表示表支持Append-Only 存储引擎。
—2.2 支持三种存储方法
• ROW,表示表的数据将以行式存储。
行存储适合于OLTP业务,适用于点查询或者增删操作比较多的场景。
• COLUMN,表示表的数据将以列式存储。
列存储适合于数据仓库业务,此类型的表上会做大量的汇聚计算,且涉及的列操作较少。
• MOT,表示表的数据将以内存的形式存储。
MOT 内存适用于高吞吐事务处理,性能瓶颈加速,消除中间层缓存,大规模流数据提取。
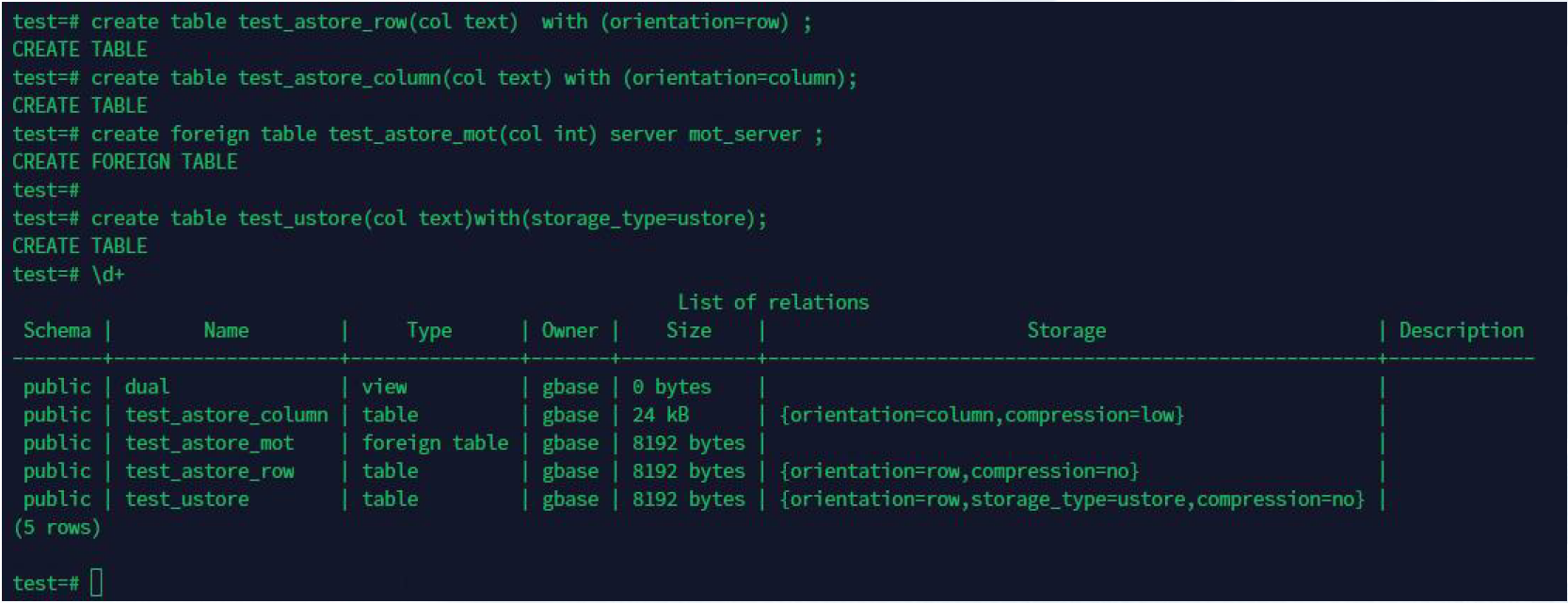
1:创建表时,指定 orientation 参数值为 row,创建行存表。
示例: create table test_astore_row(col text) with (orientation=row) ;
2:创建表时,指定 orientation 参数值为 column,创建列存表。
create table test_astore_column(col text) with (orientation=column);
3:创建表时,create foreign table ... server 为 mot_server时,创建内存表。
create foreign table test_astore_mot(col int) server mot_server ;
4:创建表时,指定 storage_type 参数值为 ustore,创建 ustore 表。
create table test_ustore(col text) with (storage_type=ustore);
当sql语句不做指定时,默认使用 astore 存储引擎,row 存储方法。
—2.3 示例
3 分区表
—3.1 介绍
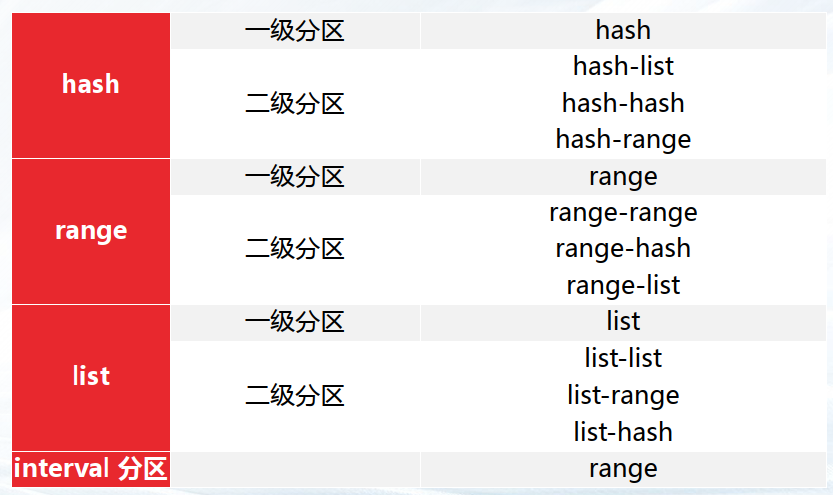
GBase 8c 需要将数据按照一定规律分布到各个数据节点,目前支持 hash 分片。
在此基础上,分区表功能,支持二级分区,9种分区组合,interval 分区。即 分片+分区 功能。
—3.2 表分片
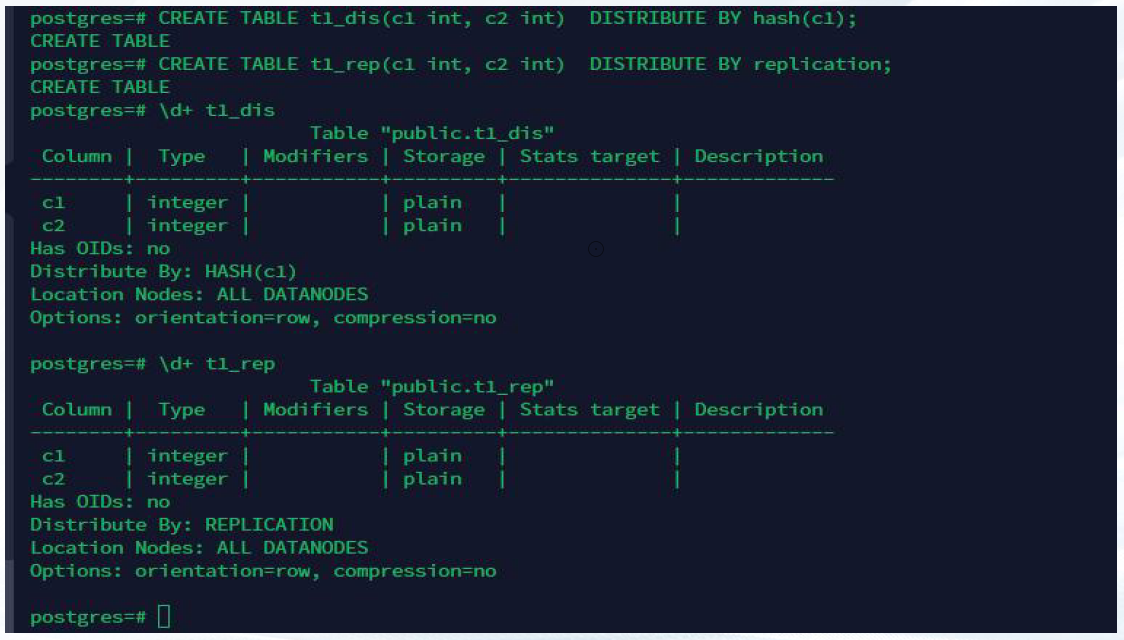
GBase 8c的数据分片策略:在创建表时,通过关键字distribute/replication 来设置表分片策略。
1:通过distribute by hash 创建 hash 分片表,将数据通过hash算法 均匀存储到每个数据节点。
CREATE TABLE t1_dis(c1 int, c2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(c1);
2:通过distribute by replication 创建 复制表,每个数据节点都会存储一份数据。
CREATE TABLE t1_rep(c1 int, c2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY replication;
备注:在不指定时,默认使用hash分片,分布式键按照顺序为第一个满足hash算法的字段。
示例:
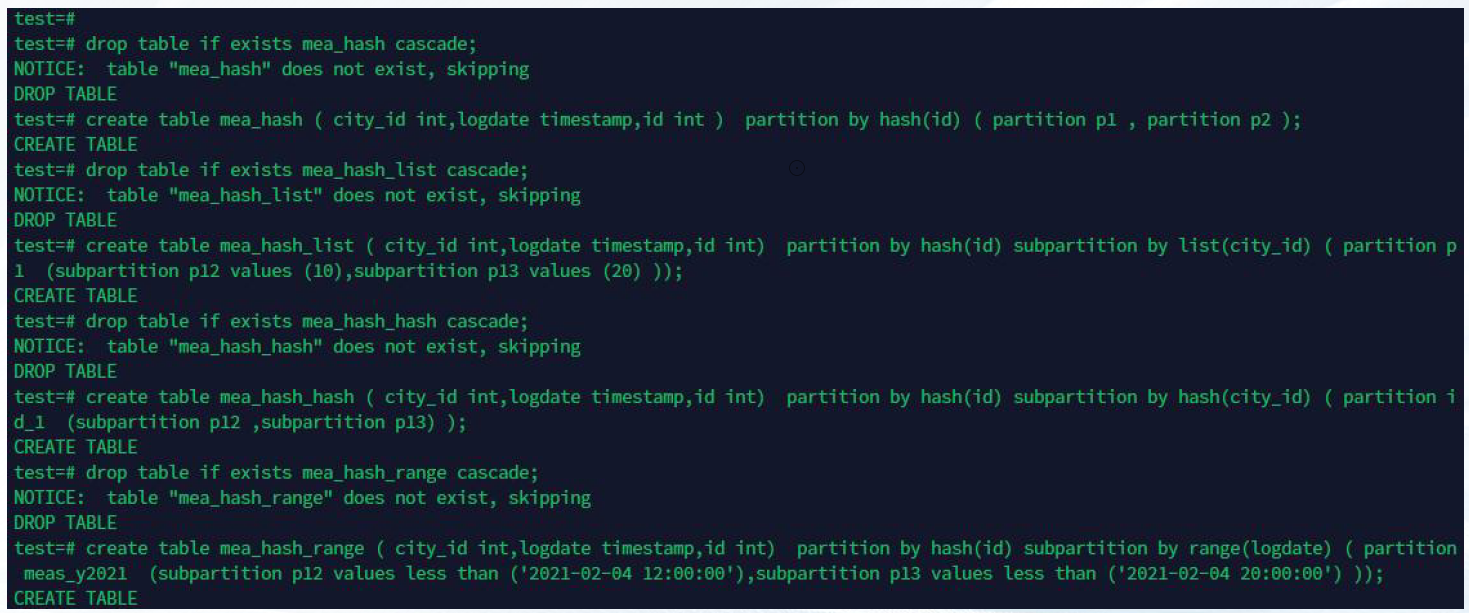
—3.3 hash 分片
hash 分片,hash 一级分区,hash-list,hash-hash,hash-range 二级分区
分区示例如下:
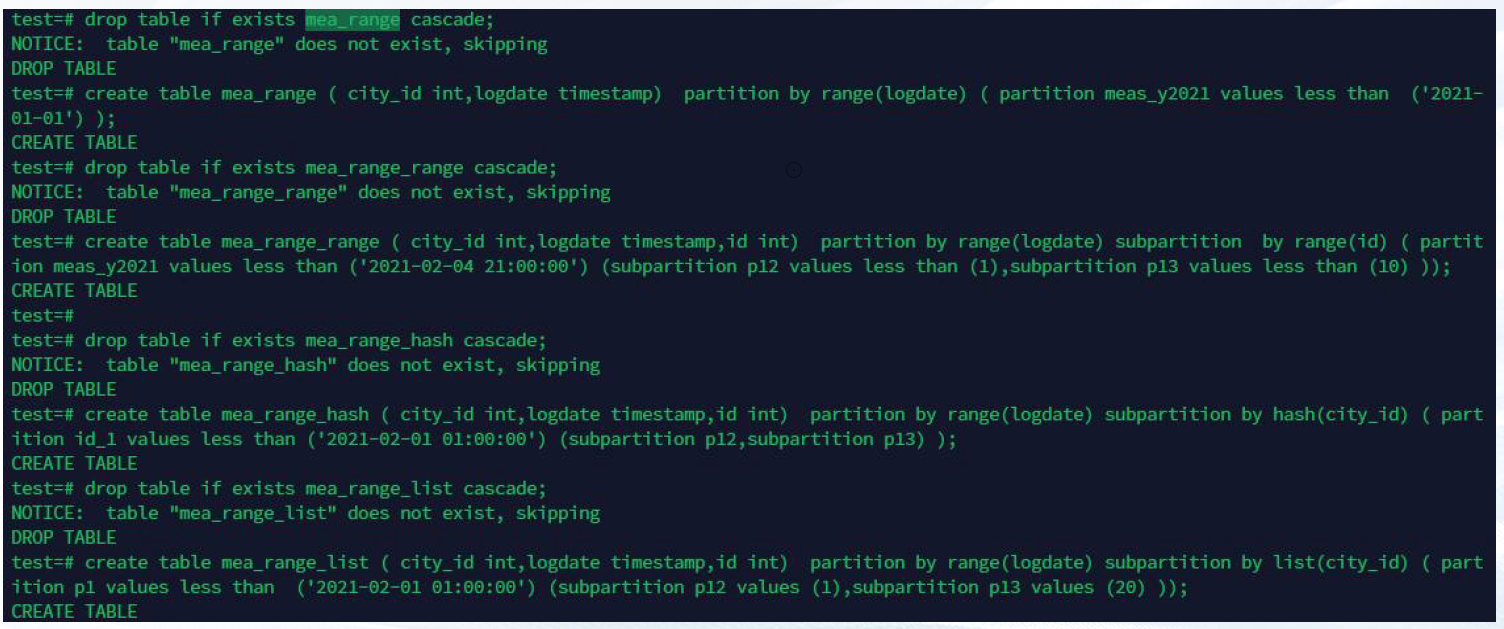
—3.4 range分区
hash 分片,range 一级分区,range-range,range-hash,range-list 二级分区。
分区示例如下:
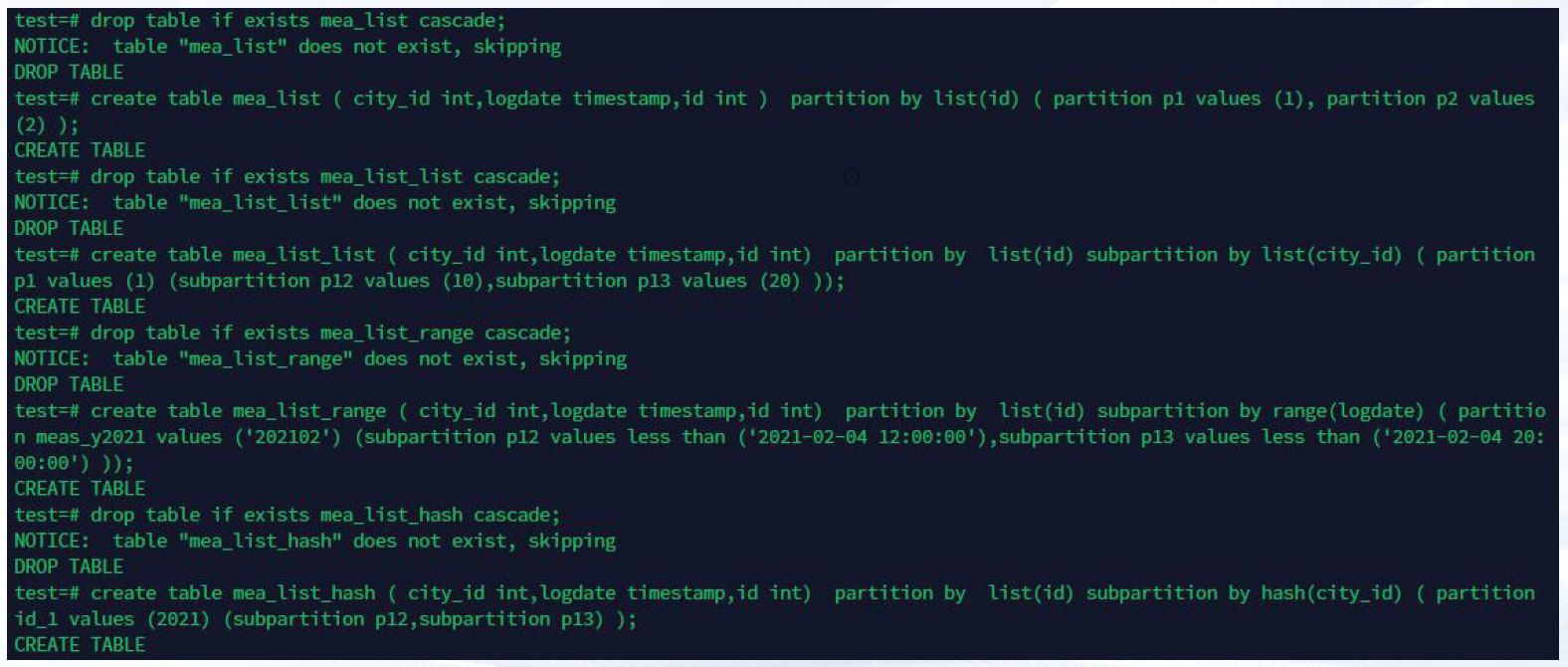
—3.5 list分区
hash分片,list一级分区,list-list,list-range,list-hash 二级分区
分区示例如下:
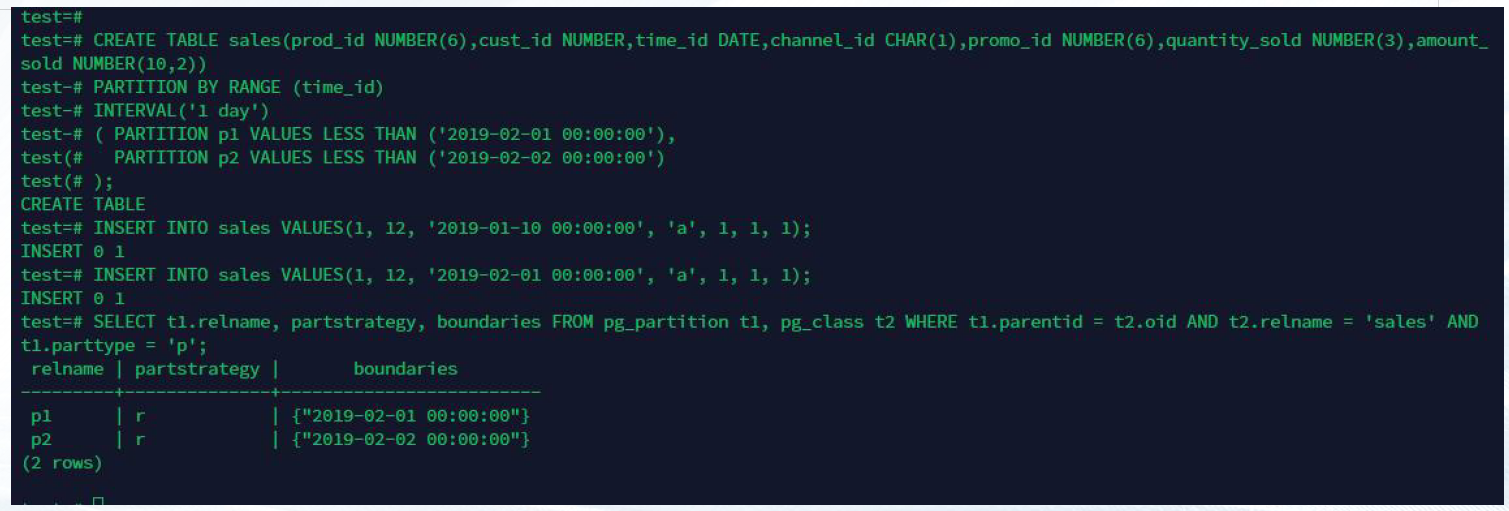
—3.6 interval 分区
interval 分区:根据间隔自动创建分区,例如:1 day、1 month。(主备式)
CREATE TABLE sales(prod_id NUMBER(6),cust_id NUMBER,time_id DATE,channel_id
CHAR(1),promo_id NUMBER(6),quantity_sold NUMBER(3),amount_sold NUMBER(10,2))
PARTITION BY RANGE (time_id) INTERVAL('1 day')
( PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN ('2019-02-01 00:00:00'),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN ('2019-02-02 00:00:00')
);
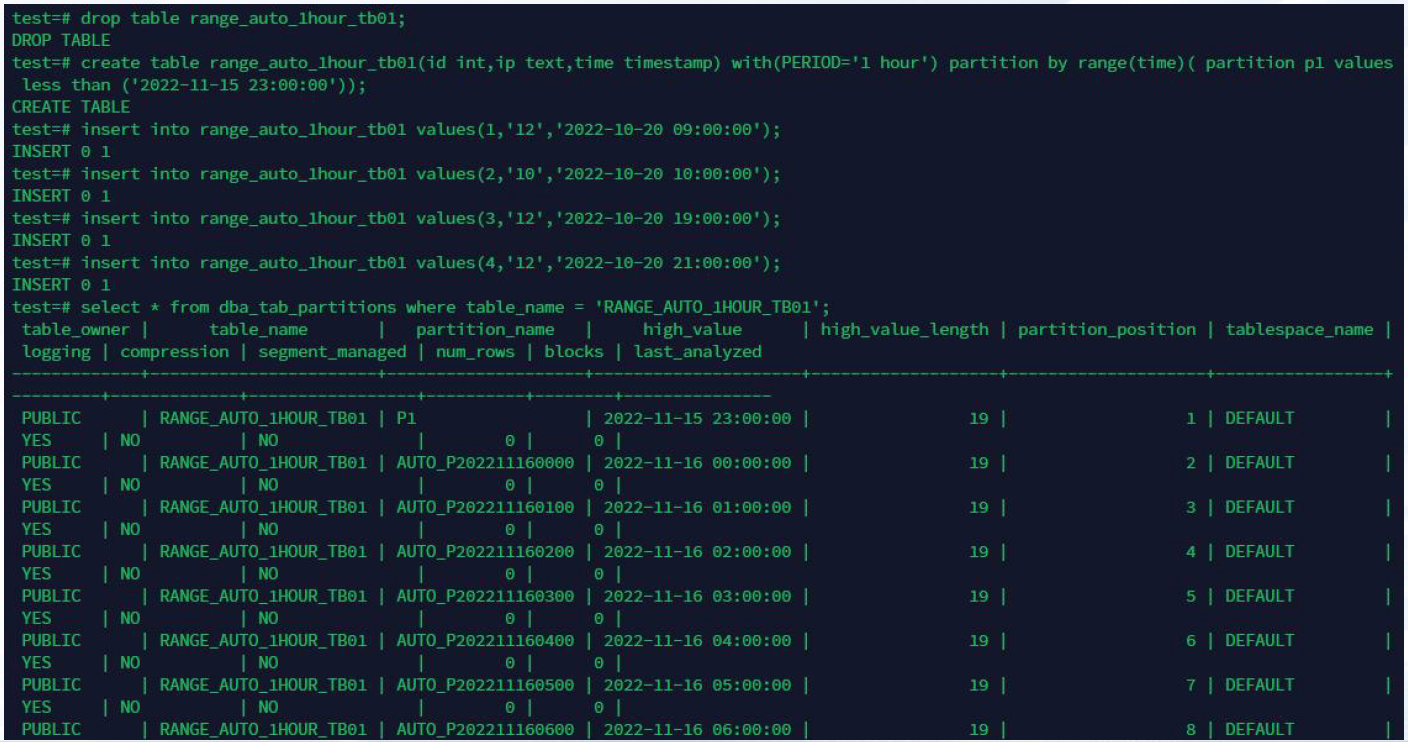
—3.7 分区自动管理
分区自动管理:根据间隔自动创建分区,例如:1 day、1 month。(分布式)
语法:建表时增加 WITH, 或者通过 ALTER TABLE xxx SET (PERIOD='1 day')来实现。
(其中 PERIOD范围是 1 hour ~ 1 year)。通过ALTER TABLE xxx RESET (PERIOD)来关闭。
限制:仅支持RANGE分区的一级分区表 (其他分区类型,以及带有二级分区的表不支持)
效果:从当前命令时间(向下规约到hour)算起,连续增加能覆盖30个period时间范围 的分区,每个分区大小为period。如果现有分区在待新增的分区范围内,则跳过此新增分 区。且每隔period时间后再次执行此流程。
create table range_auto_1hour_tb01(id int,ip text,time timestamp)
with(PERIOD='1 hour') partition by range(time)( partition p1 values less than ('2022-11-23 14:00:00'));
示例:
4 索引类型
—4.1 介绍
GBase 8c 提供了多种索引类型:hash,B-tree,gist,gin。每一种索引类型使用了一种不同的算 法来适应不同类型的查询。
B-tree —— 适合所有的数据类型,支持排序,支持大于、小于、等于、大于或等于、小于或 等于的搜索。
hash —— 索引存储的是被索引字段VALUE的哈希值,只支持等值查询。
Gist(Generalized Search Tree) —— 即通用搜索树。可处理地理数据、图像,空间,树形图 等场景。
gin —— gin索引是“倒排索引”。应用领域是加速全文搜索。
默认情况下,create index 使用B-tree 索引并适合于大部分情况。
—4.2 B-tree 索引
btree索引常常用来进行例如大于、小于、等于这些操作。 通过语法:create index ... using btree(column) 。指定使用btree索引。
—4.3 gist 索引
地理数据、图像:如果我们想要查询在某个地方是否存在某一点,即判断地理位置的"包含“。
对于空间数据,GiST索引可以使用 R树,以支持相对位置运算符(位于左侧,右侧,包含等)。
对于树形图,R树可以支持相交或包含运算符。
通过语法:create index ... using gist(column) 。指定使用gist索引。
示例:
—4.4 gin 索引
当需要搜索多值类型内的VALUE时,适合多值类型,例如数组、全文检索、TOKEN。 (根据不同的类型,支持相交、包含、大于、在左边、在右边等搜索)。
通过语法:create index ... using gin(column) 。指定使用 gin 索引。
5 数据压缩
行存表 创建表时通过关键字 compresstype,可实现数据压缩,减少磁盘的占用。
create table test_row_compress(col text) with ( compresstype = 2, COMPRESS_LEVEL = 3);
◾ COMPRESSTYPE
行存表参数,设置行存表压缩算法。1代表pglz算法,2代表zstd算法,默认不压缩。(仅支持 ASTORE下的普通表)
取值范围:0~2,默认值为0。
◾ COMPRESS_LEVEL
行存表参数,设置行存表压缩算法等级,仅当COMPRESS_TYPE为2时生效。压缩等级越高,表 的压缩效果越好,表的访问速度越慢。(仅支持ASTORE下的普通表)
取值范围:-31~31,默认值为0。
示例:
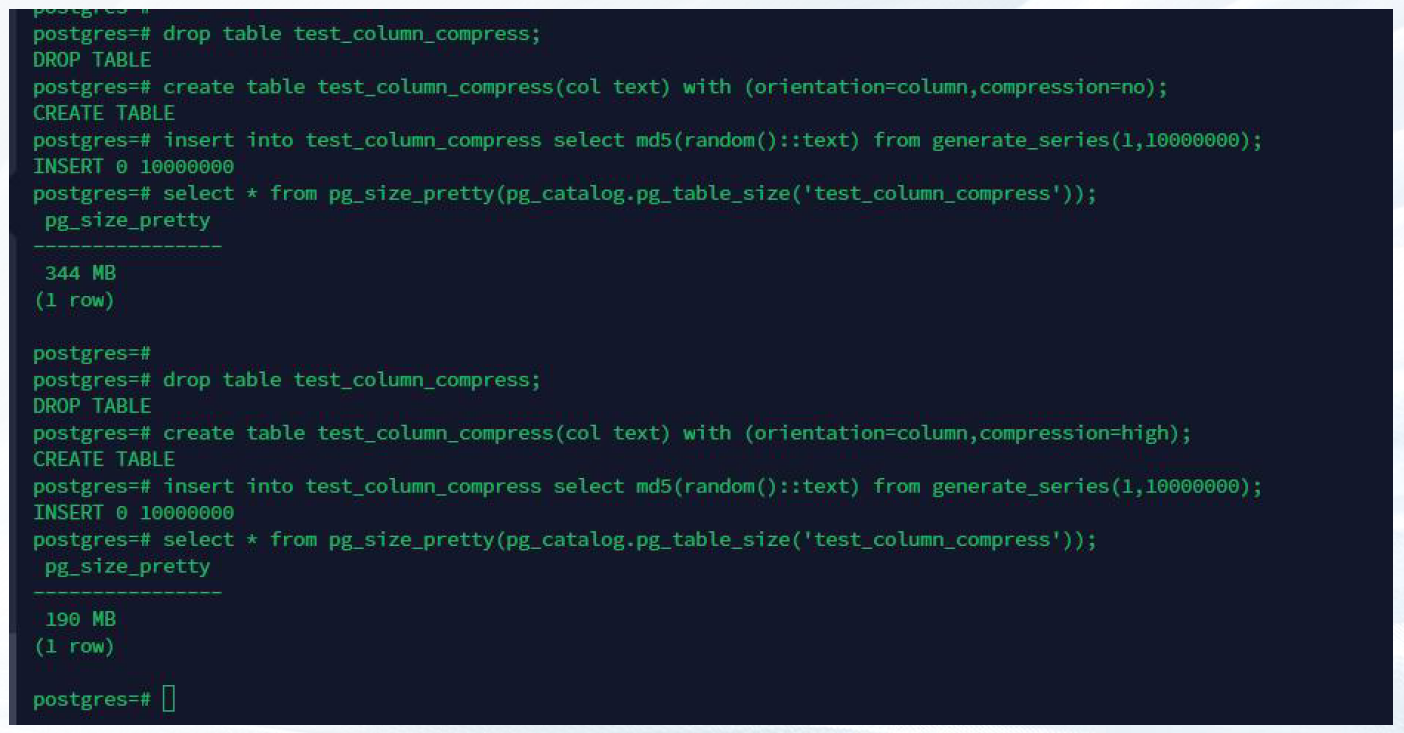
列存表 创建表时通过关键字 compression,可实现数据压缩,减少磁盘的占用。
示例:create table test_compress(col text) with (orientation=column,compression=high);
◾ COMPRESSION:
指定表数据的压缩级别,它决定了表数据的压缩比以及压缩时间。一般来讲,压缩级别越高,压 缩比也越大,压缩时间也越长;反之亦然。实际压缩比取决于加载的表数据的分布特征。行存表 不支持压缩。
取值范围:
列存表的有效值为YES/NO/LOW/MIDDLE/HIGH,默认值为LOW。
示例:
6 子事务
子事务允许你回滚部分已经事务中完成的工作。可通过关键字 SAVEPOINT,EXCEPTION, Autonomous Transaction 启动子事务。
7 自治事务
自治事务(Autonomous Transaction),在主事务执行过程中新启的独立的事务。自治事 务的提交和回滚不会影响已提交的数据,同时 自治事务也不受主事务的影响。
自治事务在存储过程,函数和匿名块中定义, 用 PARAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION 关键字来 声明。
8 操作示例
/* ***************************************************** 以下命令为 linux 命令 ************************************************** */
--- su 命令切换到数据库用户 gbase,如果当前用户已为 gbase 用户,则忽略此条命令。
su - gbase
--- linux 命令:在安装节点(即执行gha_ctl start/stop 所在的节点) 执行 gs_guc 命令 修改数据库参数
gs_guc reload -Z coordinator -N all -I all -c "enable_incremental_checkpoint=off"
gs_guc reload -Z datanode -N all -I all -c "enable_incremental_checkpoint=off"
gs_guc reload -Z gtm -N all -I all -c "enable_incremental_checkpoint=off"
gs_guc reload -Z coordinator -N all -I all -c "enable_gbase_mot=on"
gs_guc reload -Z datanode -N all -I all -c "enable_gbase_mot=on"
gs_guc reload -Z gtm -N all -I all -c "enable_gbase_mot=on"
--- linux 命令:重启数据库加载数据库参数
gha_ctl stop all -l http://192.168.1.2:2379
gha_ctl start all -l http://192.168.1.2:2379
--- linux 命令:gsql 使用默认端口 连接数据库
gsql -d postgres -r -p 15432
/* ****************************************************** 以下都为sql命令 ******************************************************* */
--- gsql 连接成功后,将以下 sql 逐条在gsql中执行,进行验证。(若使用dbeaver工具,dbeaver 连接成功后,复制粘贴以下sql 执行进行验证)
---------存储引擎
---astore
drop table if exists test_astore_row ;
drop table if exists test_astore_column ;
drop foreign table if exists test_astore_mot ;
--- 创建 astore 行存表
create table test_astore_row(col text) with (orientation=row) ;
--- 创建 astore 列存表
create table test_astore_column(col text) with (orientation=column);
--- 创建 astore 内存表
create foreign table test_astore_mot(col int) server mot_server ;
---ustore
drop table if exists test_ustore ;
create table test_ustore(col text)with(storage_type=ustore);
--- GBase 8c的数据分片策略:在创建表时,通过关键字distribute/replication 来设置表分片策略。
--- 1:通过distribute by hash 创建 hash 分片表,将数据通过hash算法 均匀存储到每个数据节点。创建hash分片
drop table if exists t1_dis ;
CREATE TABLE t1_dis(c1 int, c2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(c1);
--- 2:通过distribute by replication 创建 复制表,每个数据节点都会存储一份数据。
drop table if exists t1_rep ;
CREATE TABLE t1_rep(c1 int, c2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY replication;
-- 分区表
-- 一级 hash 分区
drop table if exists mea_hash cascade;
create table mea_hash ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int ) partition by hash(id) ( partition p1 , partition p2 );
--二级分区 hash-list,hash-hash, hash-range
drop table if exists mea_hash_list cascade;
create table mea_hash_list ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by hash(id) subpartition by list(city_id) ( partition p1 (subpartition p12 values (10),subpartition p13 values (20) ));
drop table if exists mea_hash_hash cascade;
create table mea_hash_hash ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by hash(id) subpartition by hash(city_id) ( partition id_1 (subpartition p12 ,subpartition p13) );
drop table if exists mea_hash_range cascade;
create table mea_hash_range ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by hash(id) subpartition by range(logdate) ( partition meas_y2021 (subpartition p12 values less than ('2021-02-04 12:00:00'),subpartition p13 values less than ('2021-02-04 20:00:00') ));
-- 一级 range 分区
drop table if exists mea_range cascade;
create table mea_range ( city_id int,logdate timestamp) partition by range(logdate) ( partition meas_y2021 values less than ('2021-01-01') );
--二级 range-range, range-hash,range-list
drop table if exists mea_range_range cascade;
create table mea_range_range ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by range(logdate) subpartition by range(id) ( partition meas_y2021 values less than ('2021-02-04 21:00:00') (subpartition p12 values less than (1),subpartition p13 values less than (10) ));
drop table if exists mea_range_hash cascade;
create table mea_range_hash ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by range(logdate) subpartition by hash(city_id) ( partition id_1 values less than ('2021-02-01 01:00:00') (subpartition p12,subpartition p13) );
drop table if exists mea_range_list cascade;
create table mea_range_list ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by range(logdate) subpartition by list(city_id) ( partition p1 values less than ('2021-02-01 01:00:00') (subpartition p12 values (1),subpartition p13 values (20) ));
-- 一级 list 分区
drop table if exists mea_list cascade;
create table mea_list ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int ) partition by list(id) ( partition p1 values (1), partition p2 values (2) );
--期望支持.成功执行
-- 二级 list-list,list-range,list-hash 分区
drop table if exists mea_list_list cascade;
create table mea_list_list ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by list(id) subpartition by list(city_id) ( partition p1 values (1) (subpartition p12 values (10),subpartition p13 values (20) ));
drop table if exists mea_list_range cascade;
create table mea_list_range ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by list(id) subpartition by range(logdate) ( partition meas_y2021 values ('202102') (subpartition p12 values less than ('2021-02-04 12:00:00'),subpartition p13 values less than ('2021-02-04 20:00:00') ));
drop table if exists mea_list_hash cascade;
create table mea_list_hash ( city_id int,logdate timestamp,id int) partition by list(id) subpartition by hash(city_id) ( partition id_1 values (2021) (subpartition p12,subpartition p13) );
------------数据库分区查看
with RECURSIVE temp_partition as(
SELECT t1.oid, t1.relname, partstrategy, boundaries,t1.parttype FROM pg_partition t1, pg_class t2 WHERE t1.parentid = t2.oid AND t2.relname = 'mea_hash_hash'
union
SELECT t1.oid, t1.relname, t1.partstrategy, t1.boundaries,t1.parttype FROM pg_partition t1 join temp_partition t2 on t1.parentid = t2.oid where t2.parttype='p')
select t1.relname, t1.partstrategy, t1.boundaries,t1.parttype from temp_partition t1;
--- 自动分区功能,请注意:创建分表时,子分区必须要有一个 大于当前时间 2小时的 分区。时间需按照实际时间 进行修改。
create table range_auto_1hour_tb01(id int,ip text,time timestamp) with(PERIOD='1 hour') partition by range(time)( partition p1 values less than ('2023-02-23 19:00'));
select * from dba_tab_partitions where table_name = 'RANGE_AUTO_1HOUR_TB01';
insert into range_auto_1hour_tb01 values(1,'12','2023-2-18 09:00:00');
insert into range_auto_1hour_tb01 values(2,'10','2023-2-18 10:00:00');
insert into range_auto_1hour_tb01 values(2,'10','2023-2-19 18:00:00');
insert into range_auto_1hour_tb01 values(2,'10','2023-2-19 19:00:00');
--多种索引
--hash 索引
create table rw_split(col int,name text);
insert into rw_split select generate_series(1,50000), md5(random()::text)::text;
create index rw_split_col_hash on rw_split using hash(col);
explain select * from rw_split where col =2;
-----------------btree 索引
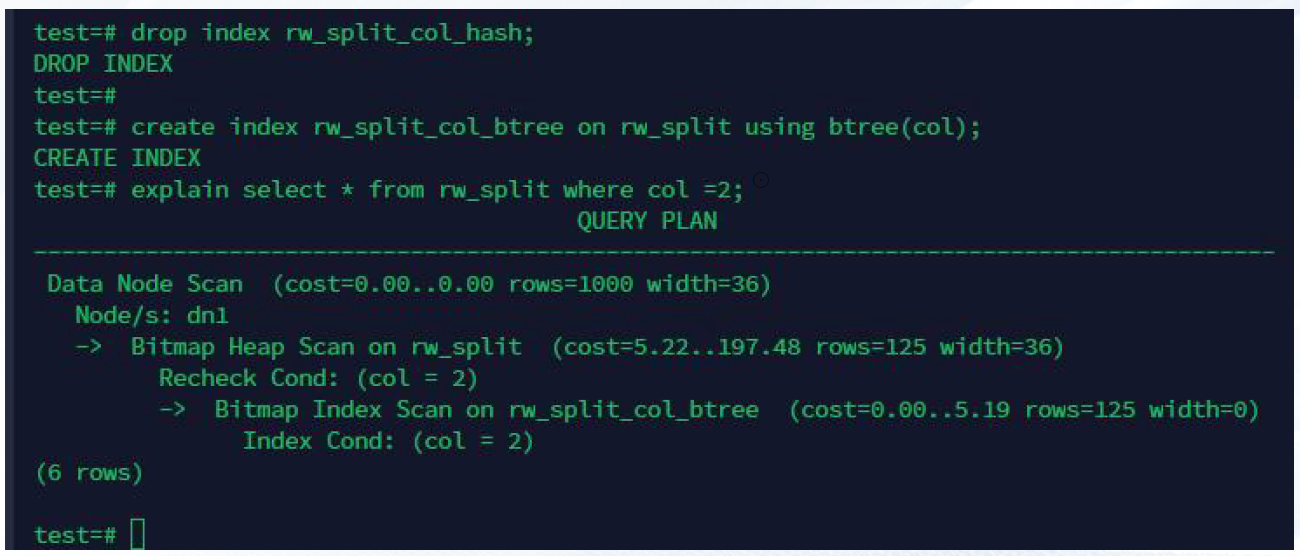
drop index rw_split_col_hash;
create index rw_split_col_btree on rw_split using btree(col);
explain select * from rw_split where col =2;
---------------gist 索引
drop table if exists t_gist;
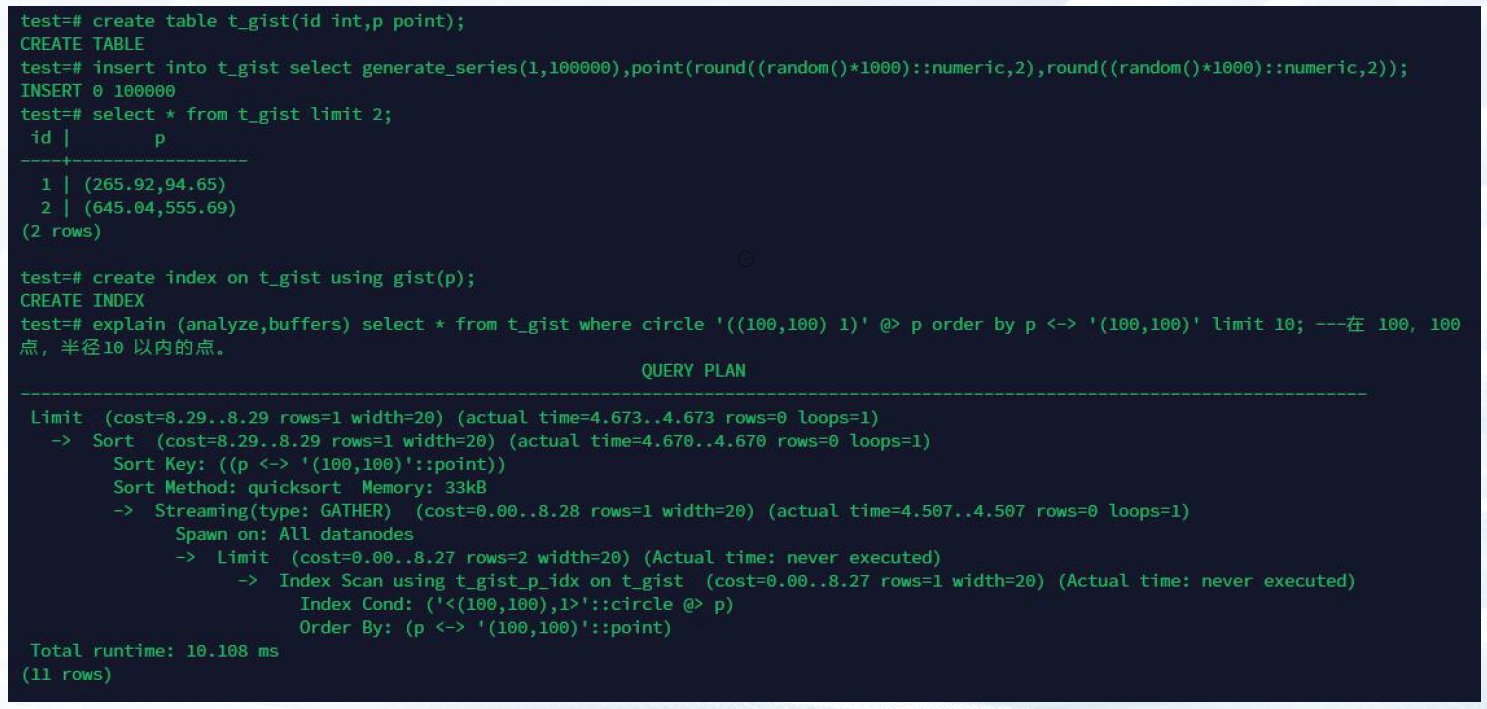
create table t_gist(id int,p point);
insert into t_gist select generate_series(1,10000),point(round((random()*1000)::numeric,2),round((random()*1000)::numeric,2));
select * from t_gist limit 2;
create index on t_gist using gist(p);
explain (analyze,buffers) select * from t_gist where circle '((100,100) 1)' @> p order by p <-> '(100,100)' limit 10; ---在 100,100 点,半径10 以内的点。
---------------gin索引
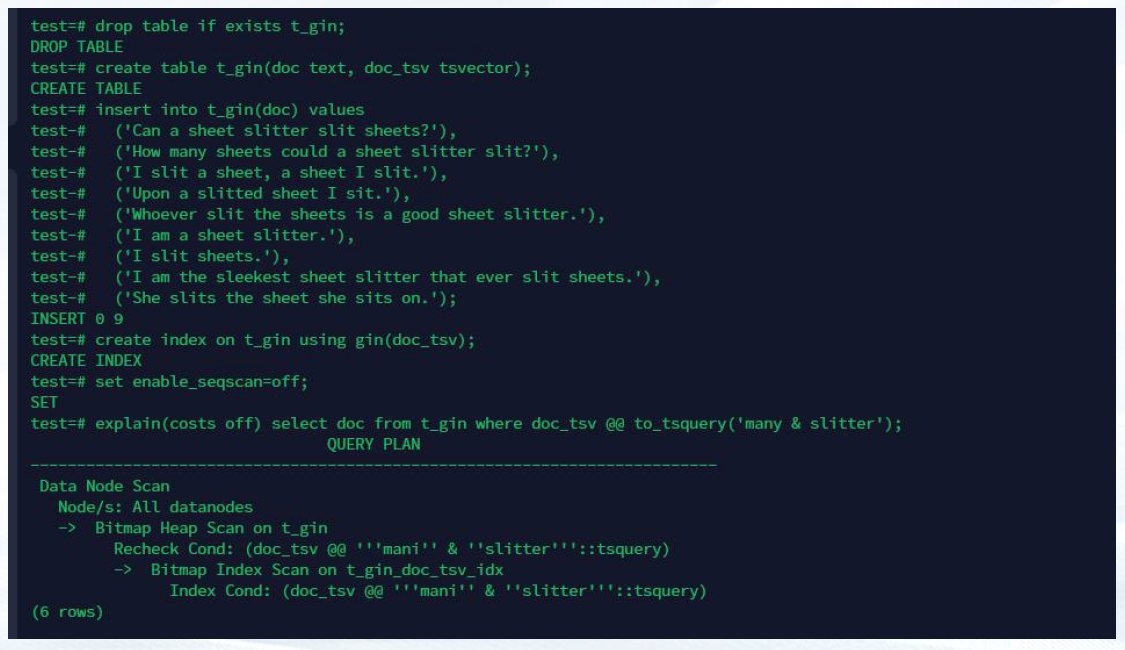
drop table if exists t_gin;
create table t_gin(doc text, doc_tsv tsvector);
insert into t_gin(doc) values
('Can a sheet slitter slit sheets?'),
('How many sheets could a sheet slitter slit?'),
('I slit a sheet, a sheet I slit.'),
('Upon a slitted sheet I sit.'),
('Whoever slit the sheets is a good sheet slitter.'),
('I am a sheet slitter.'),
('I slit sheets.'),
('I am the sleekest sheet slitter that ever slit sheets.'),
('She slits the sheet she sits on.');
update t_gin set doc_tsv = to_tsvector(doc);
create index on t_gin using gin(doc_tsv);
--- 为了效果,手动关闭顺序扫描。
set enable_seqscan=off;
explain(costs off) select doc from t_gin where doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery('many & slitter');
--------------表达式索引
create table test_expression(col int, name varchar(64));
insert into test_expression select 1,'ASDD';
insert into test_expression select 2,'ASDD';
insert into test_expression select 3,'AS';
insert into test_expression select 4,'ASsda';
insert into test_expression select 5,'ASdssa';
insert into test_expression select 6,'Asds';
insert into test_expression select 7,'Assa';
insert into test_expression select 8,'as';
explain select * from test_expression where lower(name) ='as';
create index on test_expression (name);
create index test_expression_lower on test_expression (lower(name));
explain select * from test_expression where lower(name) ='as';
-----------数据压缩
---- 行存压缩
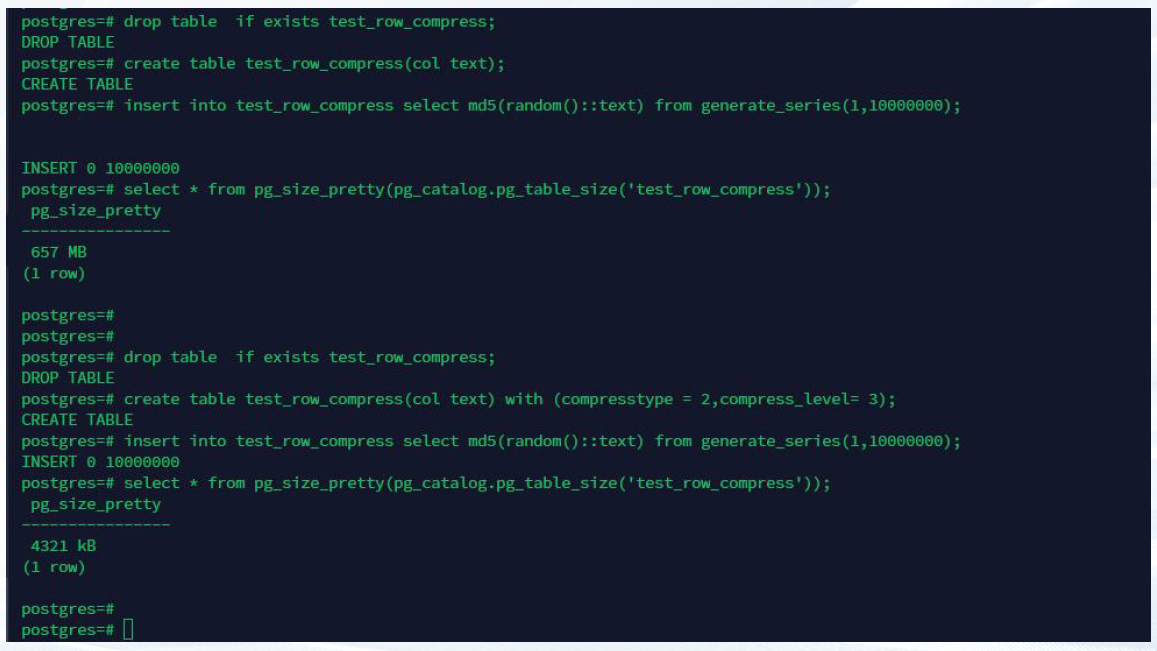
drop table if exists test_row_compress;
create table test_row_compress(col text);
insert into test_row_compress select md5(random()::text) from generate_series(1,1000000);
select * from pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_table_size('test_row_compress'));
drop table if exists test_row_compress;
create table test_row_compress(col text) with (compresstype = 2,compress_level= 3);
insert into test_row_compress select md5(random()::text) from generate_series(1,1000000);
select * from pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_table_size('test_row_compress'));
---- 列存压缩
drop table test_column_compress;
create table test_column_compress(col text) with (orientation=column,compression=no);
insert into test_column_compress select md5(random()::text) from generate_series(1,1000000);
select * from pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_table_size('test_column_compress'));
drop table test_column_compress;
create table test_column_compress(col text) with (orientation=column,compression=high);
insert into test_column_compress select md5(random()::text) from generate_series(1,1000000);
select * from pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_table_size('test_column_compress'));
----------------------子事务
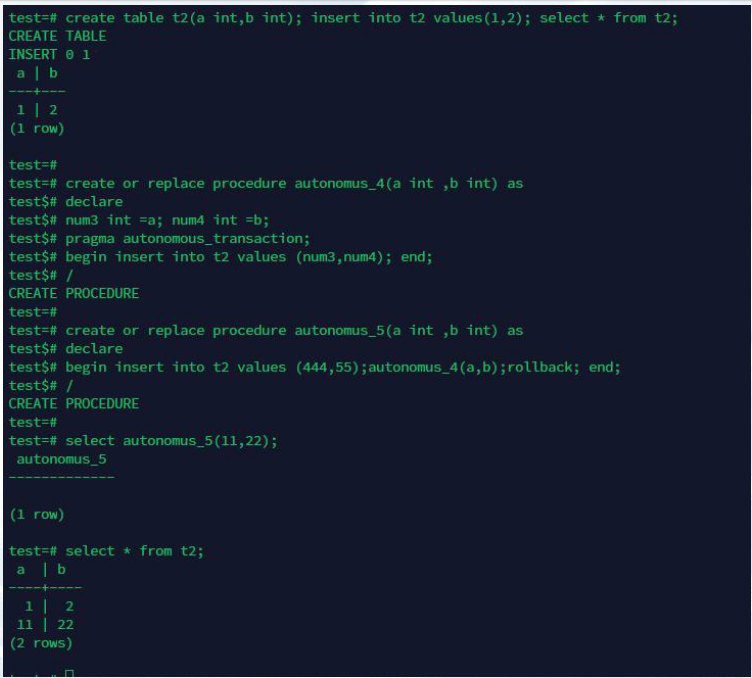
-----自治事务
create table t2(a int,b int); insert into t2 values(1,2); select * from t2;
create or replace procedure autonomus_4(a int ,b int) as
declare
num3 int =a; num4 int =b;
pragma autonomous_transaction;
begin insert into t2 values (num3,num4); end;
/
create or replace procedure autonomus_5(a int ,b int) as
declare
begin insert into t2 values (444,55);autonomus_4(a,b);rollback; end;
/
select autonomus_5(11,22);
select * from t2;
-----------savepoint
--设置保存点
--创建表
drop table if exists savepoint_test;
create table savepoint_test(a int primary key,b int) ;
--开始事务
start transaction;
--插入数据
insert into savepoint_test values(1,2);
--创建保存点
savepoint test_savepoint;
--插入数据
insert into savepoint_test values(2,2);
--查看表中数据
select * from savepoint_test;
--回滚保存点
rollback to savepoint test_savepoint;
--查看表中数据(只能查到(1,1),(2,2)被回滚)
select * from savepoint_test;
--插入数据
insert into savepoint_test values(3,3);
--提交事务
commit;
--查看表中数据(=能查到(1,1)、(3,3),(2,2)被回滚)
select * from savepoint_test;
--删除测试表savepoint_test
drop table savepoint_test;
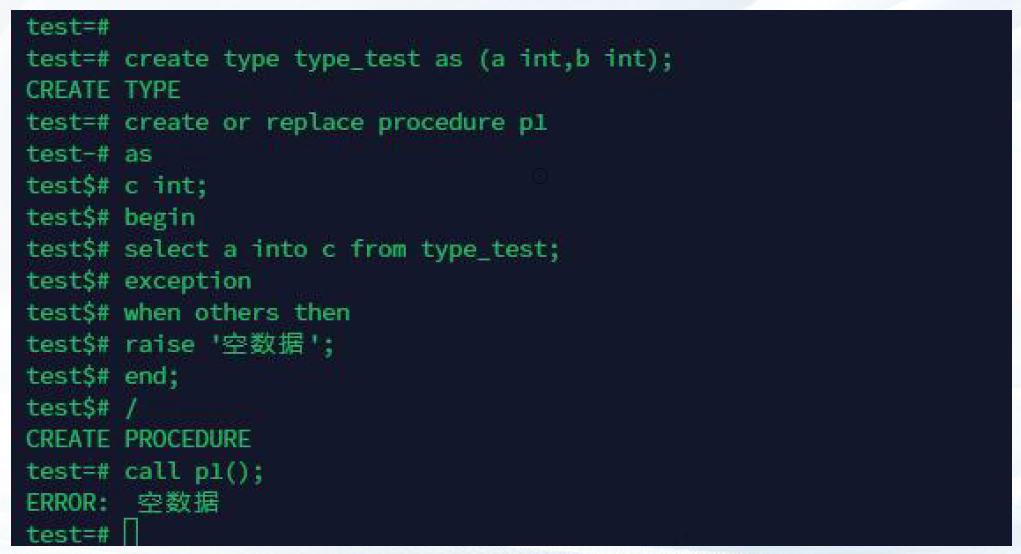
--------exception
create type type_test as (a int,b int);
create or replace procedure p1
as
c int;
begin
select a into c from type_test;
exception
when others then
raise 'NULL' ;
end;
/
call p1();
 MySQL学习笔记
MySQL学习笔记